Mortality from liver cirrhosis in Espírito Santo State, Brazil.

Mortality from liver cirrhosis in Espírito Santo State, Brazil.
Abstract
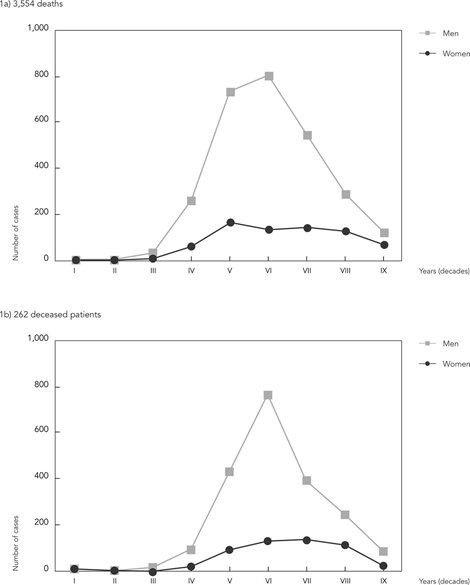
To study mortality from liver cirrhosis in Espírito Santo State, Brazil, we reviewed death certificates (DC) from 2000-2010 and medical records of deceased patients with investigation of alcoholism and hepatitis B or C. From a total of 218,410 DC, 3,554 deaths from liver cirrhosis were retrieved. The annual mortality rate was 19.8/100,000 for men and 4.31/100,000 for women, without significant changes after correction for ICD-R98 and R99 and without a significant increase in the annual percentage change. In 49% of death certificates, the aetiology of cirrhosis was defined: of these alcoholism in 81.5% of cases and viral hepatitis in 15.7%. Aetiology was confirmed in 262 reviewed records, including alcoholism (40.5%); hepatitis B or C (26.7%); other (3.8%); and cryptogenic (10.6%). The mean annual potential years of life lost were 5,946 years and 1,739 years for men and women respectively. The mortality rate from cirrhosis in Espírito Santo State is intermediate in relationship to worldwide data; alcoholism and hepatitis B or C were the main aetiologies; probably alcoholism is overestimated and hepatitis B and C viruses are underestimated as causes of cirrhosis registered on death certificates.
- PMID:
- 25099056
- [PubMed – in process]
Free full text


